Taken as a whole, fiber network infrastructure in the MENA region continues to grow steadily, but perhaps unsurprisingly, the level of fiber penetration varies from country to country.
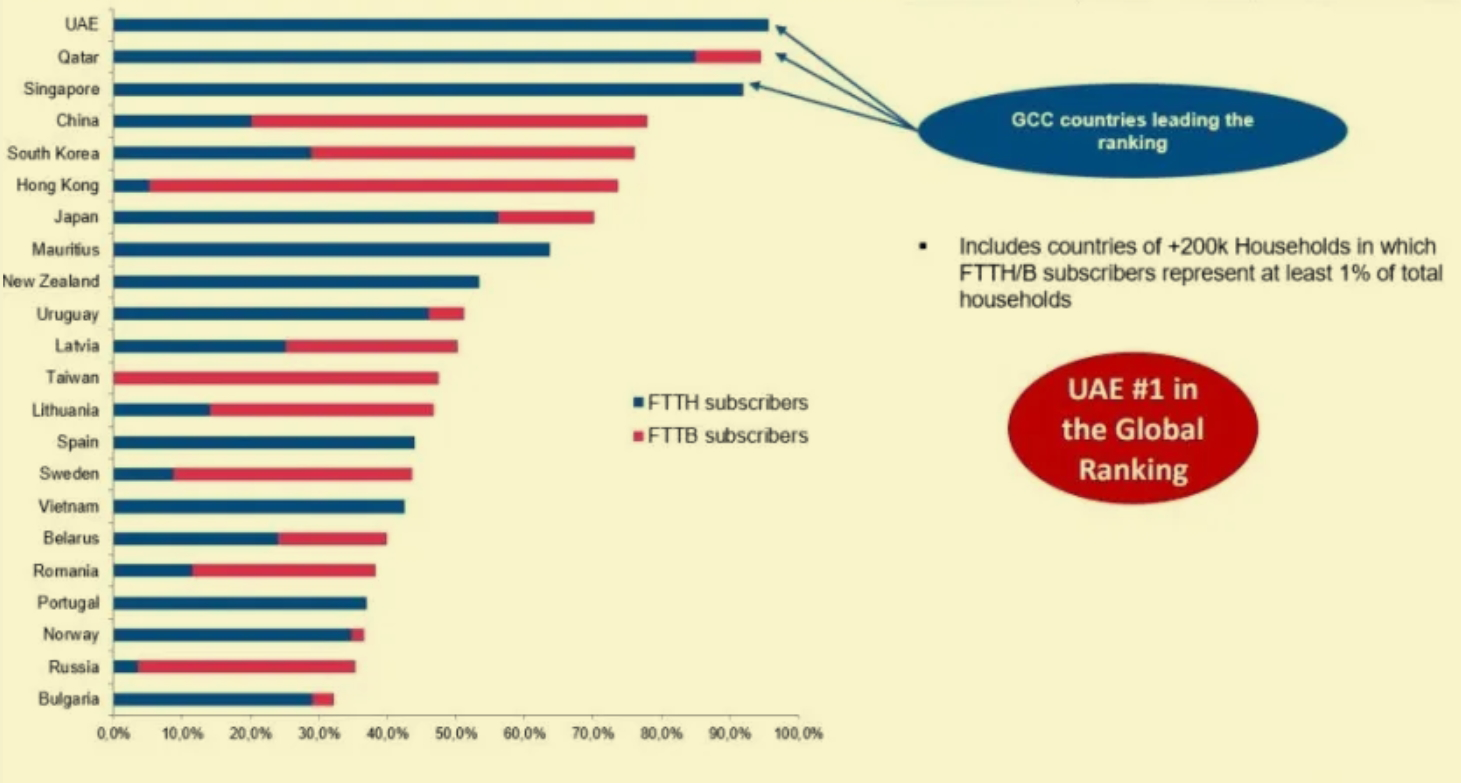
The UAE is the number one country in the world with FTTH covering 95.7% of UAE homes and its fiber network coverage exceeds that of Singapore, China, Korea, Hong Kong and Japan.
So what have been the key developments and trends in fiber network deployment in the region over the past year or so? What are the key technical, regulatory, market and operational challenges that fiber network developers in the MENA region are currently facing in expanding their fiber system deployments? What types of strategies are they adopting or planning to adopt to address these challenges?
The MENA region has "made tremendous progress" over the past year, with the United Arab Emirates (UAE) retaining its "global leadership position" in the FTTH rankings, Qatar among the top 10 globally, and Saudi Arabia's fiber-to-the-home rollout exceeding 60 percent to about 3.5 million homes.
Key trends include a range of infrastructure sharing policies being adopted across the region, as well as FTTH penetration extending beyond urban areas, with more people and more businesses viewing broadband connectivity as an economic tool.
On the technology front, we are seeing greater adaptability of new data centers and international links, and more announcements of new construction projects as more traffic is routed and localized across the region. Elsewhere, fiber network deployments are increasing significantly in the MENA region, with significant progress being made in expanding the fiber core.
Several Arab countries have launched national broadband plans to improve connectivity and facilitate digital transformation.
Overall, Arab countries that have stimulated investment and competition in national backbone infrastructure through licensing or public-private partnerships (PPPs) have been able to achieve quantum gains in fiber coverage compared to those that have relied exclusively on incumbent operator investment.
We are also seeing a trend towards using the power grid to reach more places with fiber optic technology.
Meanwhile, fiber broadband subscribers in the Middle East increased from 26.9 million in Q1 2022 to 30.5 million in Q1 2023, equivalent to an impressive 13% year-on-year growth.
Fiber broadband penetration in the MENA region grew from 7.03% in Q1 2022 to 7.78% in Q1 2023
In terms of deployed technologies, the GPON family dominates in the MENA region. In most of Africa, 2.5G GPON is being deployed and XGS-PON is also present in some countries.

The MENA region is on the global interconnection map as a whole, and in some cases is at the forefront of deployment. However, while the region is making substantial progress and benefiting from its global connectivity, he region is not uniform in terms of fiber deployment maturity and can be tentatively divided into segments.
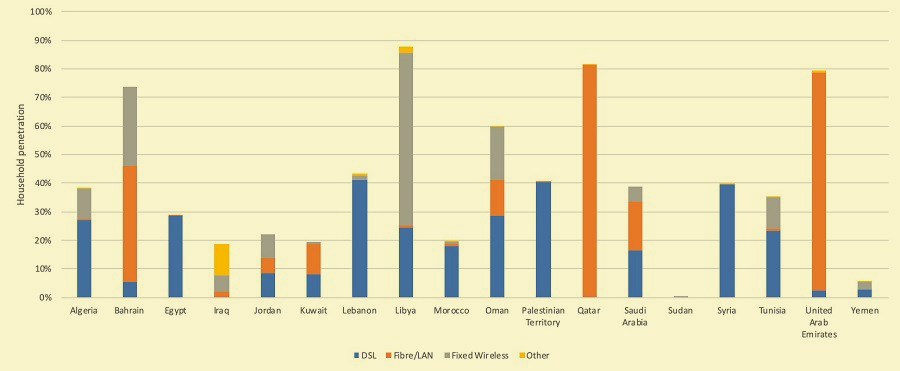
The UAE, a global leader in fiber-to-the-home, is ranked among the top 20 globally by the European Fiber-to-the-Home Council, along with Qatar and Bahrain. The mid-segment is largely driven by Saudi Arabia, with a focus on bridging the digital divide by expanding FTTH coverage across the Kingdom, followed by the likes of Oman, Kuwait and Jordan. Finally, the lower end of the market includes countries such as Egypt, Iraq, Morocco and Tunisia, which are allocating resources to provide fiber optic connectivity to their citizens.
Given the differences in deployment requirements across market segments, network architectures and solutions must be tailored to specific needs. In this regard, the key trend now is to build entirely new fiber optic networks and to upgrade existing networks with advanced technologies.
The MENA Fiber Connectivity Council estimates that more than 5.2 million homes or businesses are already connected via fiber, with FTTH remaining the technology of choice.
Another important trend in the MENA region is the growing demand for bandwidth and speed, which has fueled creativity and innovation in network construction. This puts pressure on fiber operators to find efficient, fast and reliable deployment solutions. In the dynamic business environment of the MENA region, the use of pre-connected solutions is a strategic approach to speeding up deployment, reducing administrative burdens and lowering total costs.
The main challenge facing the expansion of FTTx in the MENA region today is the development of the necessary infrastructure, which requires significant investment in equipment and cabling. Expanding fiber optic connectivity to homes and businesses in rural or less densely populated areas is often a daunting task in harder to reach areas.
While copper technology is beginning to exit the market in some countries, convincing customers in some areas to switch to fiber remains a market challenge - not least because high-speed fiber is sometimes perceived as expensive by consumers, especially in low-income households.
Meanwhile, the MENA region faces many of the same challenges as Europe and other regions, including global supply chain disruptions, inflation and soaring raw material prices in 2022, and she also noted that the MENA region is not immune to the impact of higher interest rates from central banks. In addition to these more general challenges, there are more unique challenges facing the region, whether it be foreign exchange restrictions or civil unrest elsewhere, as well as fierce competition that is affecting the return on investment for some operators.
However, some of these issues are being addressed through shared infrastructure programs or government subsidies. Manpower is not a particular challenge compared to the EU or the U.S., while regulations are being relaxed to encourage private investors to explore broadband opportunities, and a particular challenge is to find new monetization opportunities through innovation, as some legacy technologies are still competing with triple play, such as television and broadband delivered via satellite.
The various challenges that countries face in the FTTH space often depend on the stage of fiber deployment in each market. Low-maturity FTTH countries, with lower average revenue per user, face funding challenges or potentially longer payback periods, while highly mature markets struggle to accurately forecast future demand and adequately prepare their networks.
Network convergence requires a process of densification of both external and internal plant infrastructure. In addition, meeting future-proof requirements further limits the construction of networks using the latest technologies. Another obstacle is the slow pace at which regulations are adapting to market needs, which affects key areas such as expanding licensing, opening the market to private funding, and facilitating the entry of new businesses.
The region also faces a common problem of scarce skilled and experienced labor resources. To address this issue, it is imperative to develop and implement specialized vocational training programs, establish suitable facilities, and develop local expertise.
In addition to these challenges, macro-environmental factors play a crucial role in influencing the pace of new product rollout. Political and economic conditions, overall industry volatility and other external dynamics need to be factored in. Given the current abundance of these factors, it may take several years to stabilize and create a stable environment.
The exact nature and scope of fiber optic network roll-outs in the coming years will depend largely on country-specific circumstances. In particular, high-density solutions using microtrench cables in urban and highly populated areas would be preferable to overhead solutions in less densely populated areas, depending on the regulatory environment of individual countries.
There are also countries that have experience with fiber-to-the-room (FTTR) and hybrid fixed 5G broadband networks. We can also see the concept of Smart City being adopted in the planning of new cities as digital transformation continues to be highly adopted.
We expect the GCC countries (Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates) to reach a high level of maturity and near-national coverage, while others have publicly stated plans to upgrade copper networks and replace them with fiber infrastructure.
Looking ahead, the MENA region is expected to experience strong FTTx growth in the coming years. In terms of actual projections, the number of fixed broadband subscribers in the region will increase from 83.6 million by the end of 2022 to 102.3 million by the end of 2026, with the proportion of subscribers associated with FTTx connections increasing from 36% by the end of 2022 to 45% by the end of 2026, and fiber broadband penetration increasing from 7.62% by the end of 2022 to 11.60% by the end of 2028. This is because local governments and regulators are pushing for broadband development.
Based on current industry and market trends in the MENA region, there was a clear target for increased fiber deployment in local networks, driven by several factors. First, the growing demand for stable and affordable high-speed Internet has become a fundamental need. Second, growing bandwidth requirements and the need for reliable, low-maintenance connectivity have contributed to the urgency of expanding fiber infrastructure.
The rise of artificial intelligence development has further expanded the demand for processing power, requiring extensive fiber optic connectivity between servers, inside and outside data centers, and more.
To effectively meet these demands, the adoption of pre-connect solutions in high-density central server rooms has become imperative, primarily because they facilitate convergence, improve installation efficiency, optimize time and cost, enable low attenuation architectures and high bending-insensitive performance, and thus reduce overall deployment pressure.
In addition, the sustainability factor is also significant in the MENA region. Operators are prioritizing sustainability and security in their network transformation strategies, as noted in a recent report by the GSM Association.
The need to build more networks and upgrade existing ones, coupled with challenges such as the scarcity of skilled and experienced labor, as well as fast-moving trends, are triggering a shift in operators' mindset. As a result, operators of fiber deployment projects are beginning to think in terms of total cost of ownership and consider innovation, sustainability and social impact, as well as the economic cost of delays.