The evolution of Wi-Fi technology has consistently driven the advancement of wireless connectivity. Within this realm of wireless communication, the 802.11ac standard, as the fifth generation of Wi-Fi technology, has introduced more advanced functionalities and enhanced performance. However, its developmental history, technical specifications, and the challenges it faces constitute a subject worth delving into.
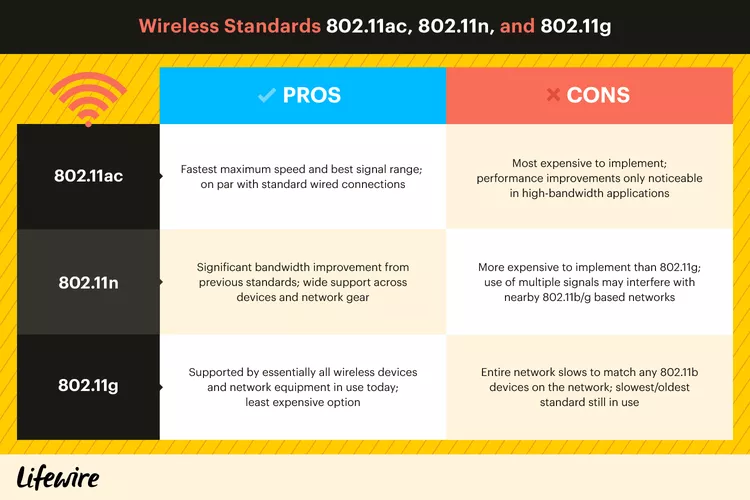
The origins of the 802.11ac standard can be traced back to 2011, with its official approval occurring in 2014. Leveraging larger signal frequency channels and more Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) radios and antennas, this technology achieves theoretical data rates of up to 1 Gbps, comparable to Gigabit Ethernet performance. This high-speed capability enables 802.11ac to support high-performance network applications like video streaming, meeting the escalating demands of users.
Differing from previous Wi-Fi standards that operated within the 2.4 GHz signal range, 802.11ac functions within the 5 GHz signal spectrum. This choice was made to circumvent common wireless interference issues at 2.4 GHz and to enable wider signaling channels compared to 2.4 GHz. To maintain backward compatibility with older Wi-Fi products, 802.11ac routers also encompass support for the 802.11n-style 2.4 GHz protocol.
802.11ac introduced beamforming technology to enhance the reliability of Wi-Fi connections in congested areas. This technology allows Wi-Fi radios to target signals towards specific directions of receiving antennas, rather than widely broadcasting signals as standard radios do. Alongside beamforming technology, the standard specifies other optional features such as wider signal channels and additional ambiguous items, providing users with more choices and flexibility.
Despite the significant performance improvements and new functionalities brought by the 802.11ac standard, it faces challenges. Consumer acceptance of upgrading network devices isn't always high, with many individuals not immediately transitioning from 802.11g or 802.11n, as the older standards remain effective in meeting basic requirements.
Furthermore, to fully harness the advantages of 802.11ac, both connecting devices need to support the new standard. While 802.11ac routers swiftly entered the market, the integration of chips supporting this standard into smartphones and laptops takes longer, potentially limiting the widespread adoption of this technology by users.
The rollout of the 802.11ac standard marks another leap forward in Wi-Fi technology. It offers users faster speeds and more reliable connections, meeting the ever-growing demands of today's networks. However, its adoption and acceptance still face challenges, necessitating collaborative efforts from the industry and users to promote its extensive application and development.
The future of Wi-Fi technology will continue to progress, and the 802.11ac standard is just one milestone in the evolutionary process of wireless communication. With ongoing technological advancements and innovations, we can anticipate more advanced, faster, and more stable Wi-Fi connections, facilitating better global connectivity.
Discussions about the impact of this standard on the wireless communication field and its future development are ongoing. The emergence of 802.11ac is just one phase in this prolonged journey.